For Which Process Are the Dna Nucleotides Used
The process by which DNA is copied. DNA replication occurs in a series of five steps.
Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy
The nucleotide is the basic building block of these molecules and is essentially are assembled by the cell one at a time and then strung together by the process of either replication in the form of DNA or what we call transcription when youre making RNA.

. The temporal process used to describe substitutions between nucleotides is a continuous-time Markov process with the four nucleotides as the states. A type of RNA synthesized from DNA that attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm and specifies the primary structure of a protein. It includes technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases.
DNA replication is an essential part of cell division as it ensures that each new cell has the same genetic information. A replication _____ is the area that results after the double helix separates during replication. Would appreciate answer with drawing as well as written explanation.
DNA untwists makes an exact copy of itself before the cell divides. This is significant in some organs since some tissues cannot be synthesised from scratch. Use terms primer template DNA nucleotides and DNA polymerase.
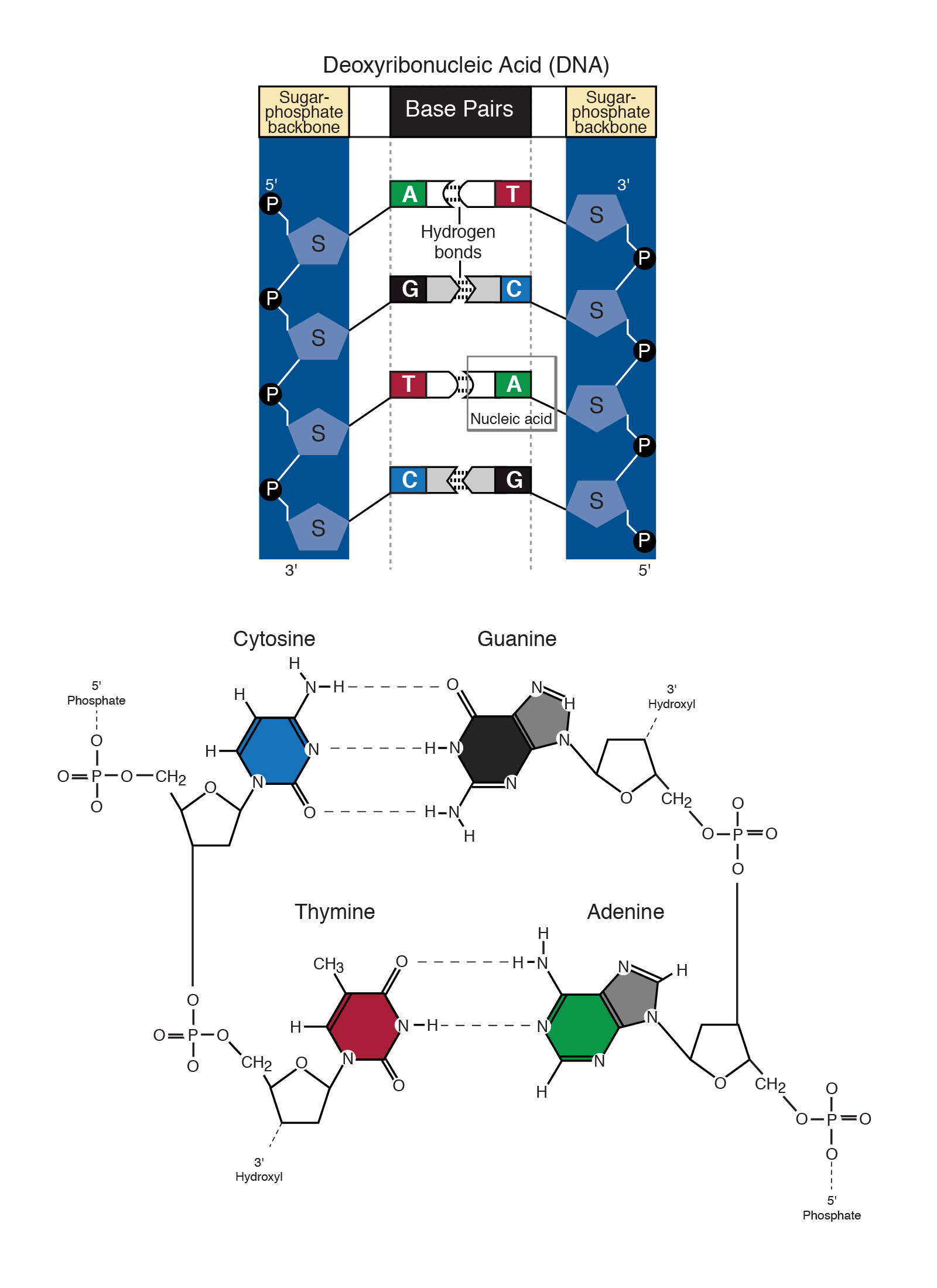
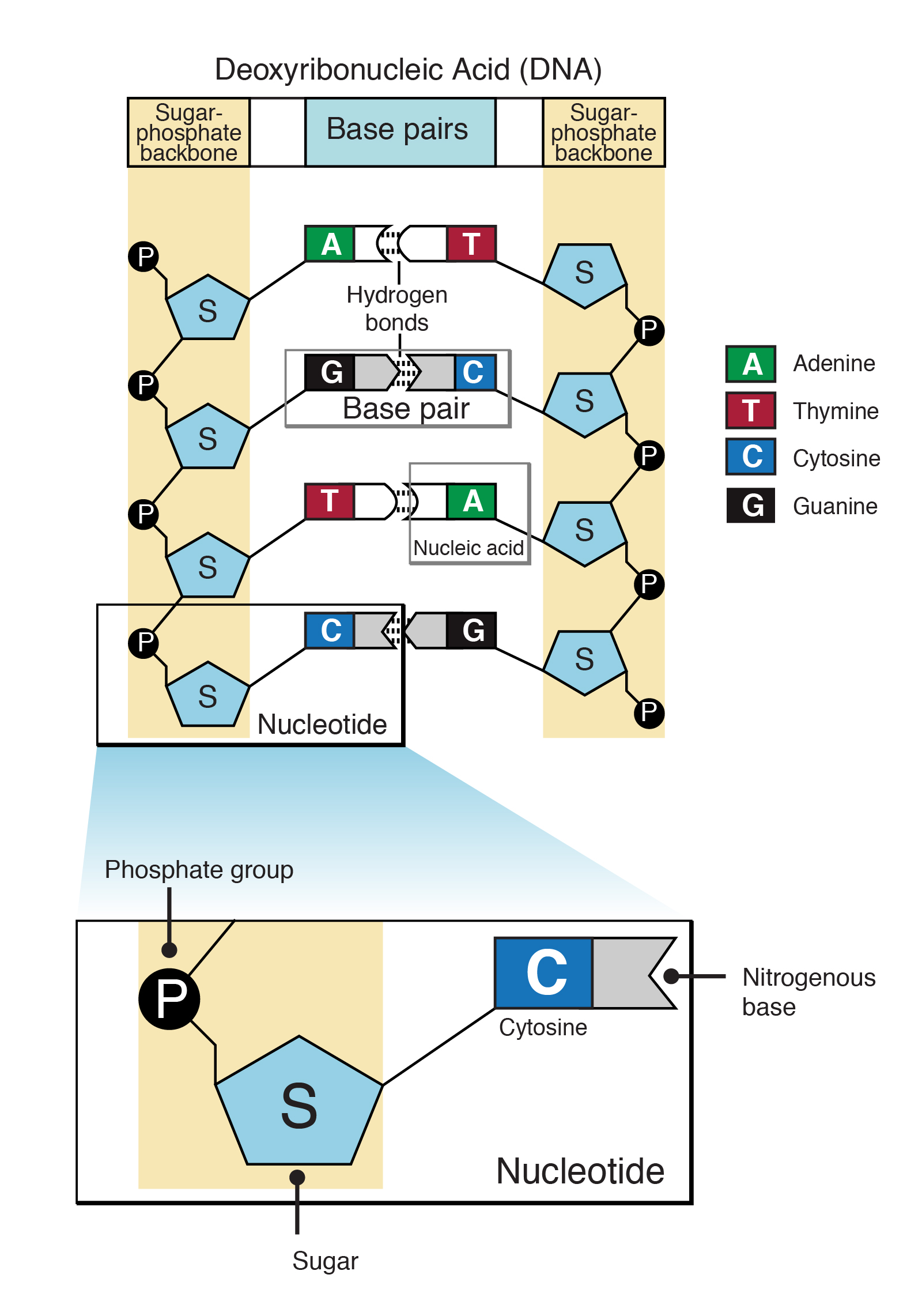
Exonucleases - group of enzymes that remove nucleotide bases from the end of a DNA chain. Complementary nucleotides base pair with those of the old strand. It is also necessary for evolution and immune system response.
The DNA of interest is purified and extracted. One of the key molecules in DNA replication is the enzyme DNA polymerase. DNA sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of nucleotides within a DNA molecule.
B RNA polymerase moves along the template strand of DNA adding complementary RNA nucleotides extending the mRNA. The technology of DNA sequencing was made faster and. Order the following choices to examine the process of transcription.
Enzyme that adds nucleotides to exposed nitrogen bases. A RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA at the promoter site and begins to transcribe the template strand of DNA. DNA replication refers to the process of duplicating DNA double strands before cell division.
After the DNA double helix unwinds each old strand serves as a template for the formation of a new strand. DNA is shattered into. A nucleotide is the building block of nucleic acid in the process of DNA and RNA formation.
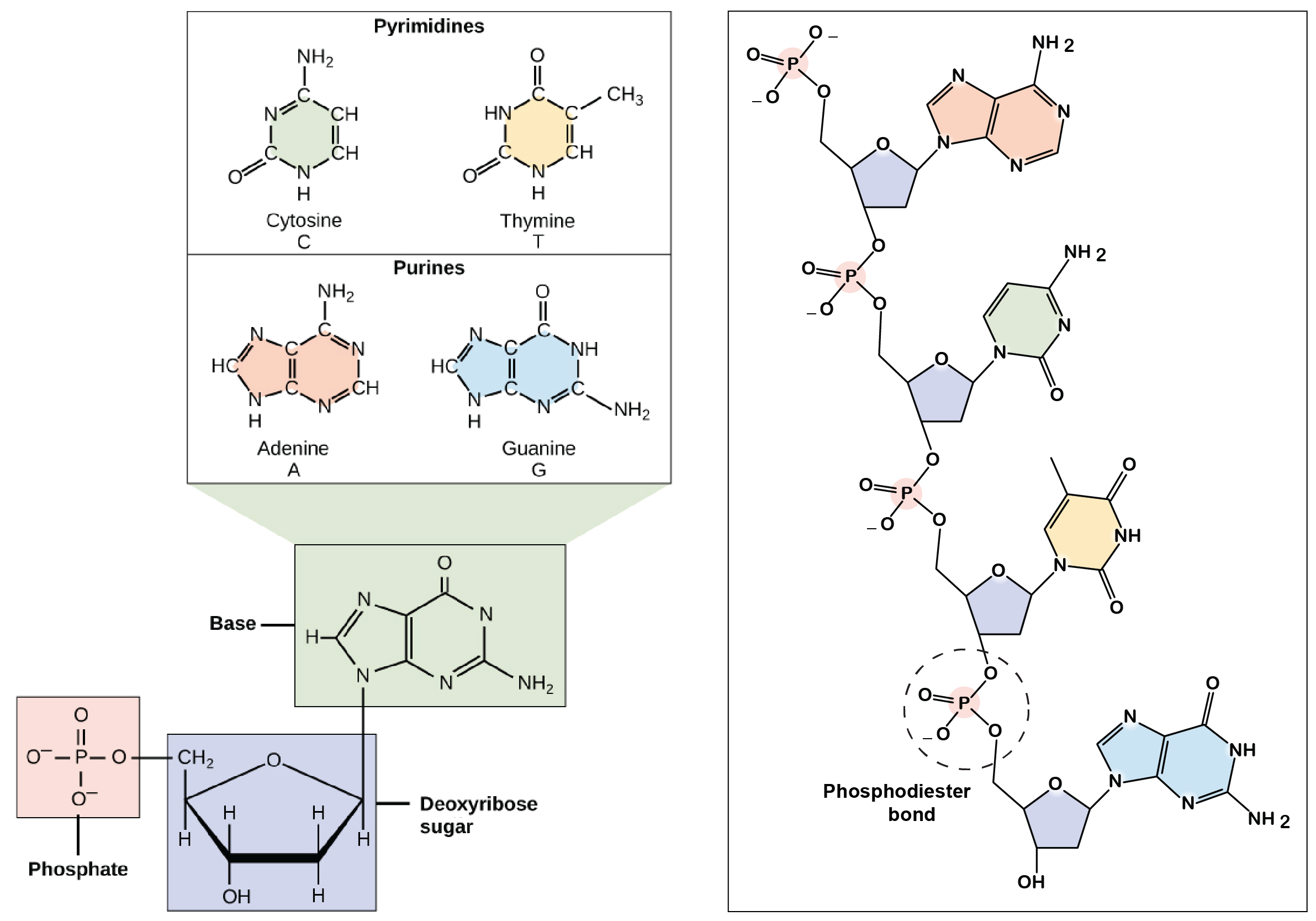
Adenine guanine cytosine and thymine in a strand of DNA. They perform various functions like metabolism enhancement enzyme reactions and cell signaling during the process of the formation of nucleic acid. Nucleotides are materials used in the DNA Synthesizer for the Extinct Species Revival Process.
Nucleotides cannot be added to the phosphate 5 end because DNA polymerase can only add DNA nucleotides in a. DNA replication is achieved by a process called semiconservative replication meaning that each new double helix includes an old strand from the parent DNA and a new strand. DNA polymerases - synthesize new DNA molecules by adding nucleotides to leading and lagging DNA strands.
In turn folic acid serves as a single carbon methyl donor in the synthesis of nucleotides. Bases and nucleosides that are generated during the breakdown of RNA and DNA are recovered via nucleotide salvage processes. In this pathway thymidine and hypoxanthine are recycled into new nucleotides.
They are crafted by smelting water bottles which is shown to the right. The 3 carbon of first nucleotide deoxyribose sugar is attached with the 5 carbon of the second nucleotide making the polynucleotide DNA helix. We describe a model for the evolution of DNA sequences by nucleotide substitution whereby nucleotide sites in the sequence evolve over time whereas the rates of substitution are variable and correlated over sites.
Explain the polymerase chain reaction process. The DNA base sequence carries the information a cell needs to assemble protein and RNA molecules. The result of duplication is that one double strand becomes two identical double strands and each double strand is the same as the original double strand.
DNA polymerases are responsible for synthesizing DNA. This method is also known as the chain termination method. The classic de novo pathway is a complex pathway that produces folic acid.
It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases. The nucleotides are attached to each other by creating phospho-diester bonds between the deoxyribose sugar and the phosphate group of every first and second nucleotides. They add nucleotides one by one to the growing DNA chain incorporating only those that are complementary to the template.
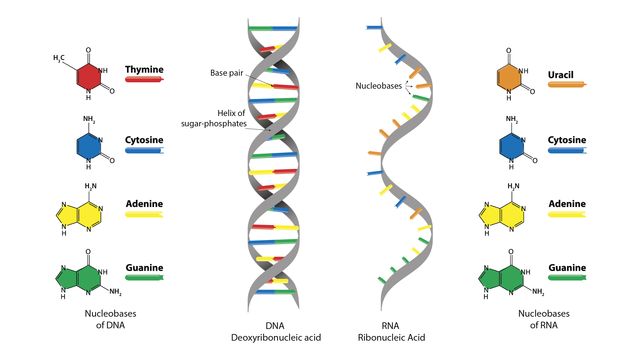
They store the genetic information in the nucleic acids that are formed during the process. Community content is available under CC. Adenine guanine cytosine and thymine.
Walk through the the process for how nucleotides and ribose are made and show how these come together to make ATP used for DNA replication. Terms in this set 21 what is the function of DNA. DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence the order of nucleotides in DNA.
You must start from glucose and CO2 as your starting materials everything else must be made from these compounds. Topoisomerase or DNA Gyrase - unwinds and rewinds DNA strands to prevent the DNA from becoming tangled or supercoiled. This problem has been solved.
The nucleic acid salvage pathway provides a second conduit for DNA synthesis. DNA sequence information is important to scientists investigating the functions of genes. DNA sequencing is a laboratory technique used to determine the exact sequence of bases A C G and T in a DNA molecule.
They are necessary to create Species DNA Test Tubes. Initiation at the origin of replication unwinding to expose the strands synthesis on both strands with many enzymes adding nucleotides 3 to 5. Use terms primer template DNA nucleotides and DNA polymerase.
The nucleotides can then be made from the recovered goods. This process is successfully completed through a mechanism called semi-reserved replication. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery.
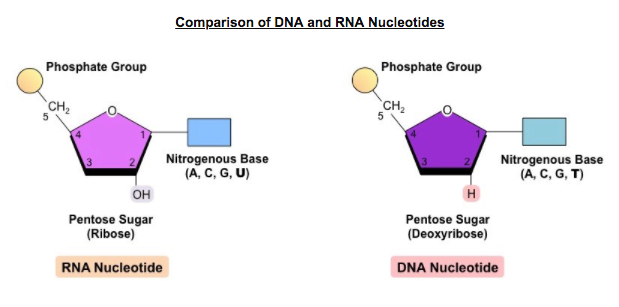
Theres an A C G and T in DNA and in RNA theres the same three nucleotides as DNA and then the T is replaced with a uracil. The term double _____ is used to describe the shape of DNA. Dna determines what traits are passed on to the next generation.
DNA polymerase will add the free DNA nucleotides using complementary base pairing A-T and C-G to the 3 end of the primer this will allow the new DNA strand to form. Creation of multiple copies of DNA. The nucleic acid that is used in key metabolic processes for all steps of protein synthesis Messenger RNA.
Five-carbon sugar found in DNA nucleotides.
9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Dna Nucleotides And Dehydration Synthesis Biochemistry School Resources Biology

Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology

Pin On What Are Dna And Dna Replication

Dna Quiz Dna Quiz Middle School Science Class Middle School Science
Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks

Dna Molecules Nucleotides Ancestrydna Learning Hub
The Structure And Function Of Dna Ent Audiology News

Dna Sequencing Animation Dna Sequencing Is The Process Used To Determine The Exact Sequence Of The Nucleotides In A Strand Of D Dna Synthesis Sequencing Dna

1 What Are The 3 Components Of This Dna Nucleotide 2 What Is The Function Of Dna In The Cell Ppt Download

A Table Lists 64 Different Combinations Of The Nucleotides Uracil U Cytosine C Adenine A And Guanine G Teaching Biology Learning Science Biochemistry




Comments
Post a Comment